THE WORLD GAME OF ECONOMICS: LESSON 7
Focus on Monetary Policy
NOTE: It is highly recommended that you read over this entire lesson before you begin.
Preliminary Discussion: Monetary policy refers to the control of a nation's money supply, interest rates, and banking regulations. The central bank of a country can use monetary policy as a counter-cyclical tool, because changes in the money supply and interest rates affect aggregate demand and aggregate supply. Generally, monetary policy is not subject to political constraints and has more flexibility than fiscal policy. However, monetary policy works through a series of decision-making linkages, so there can be a relatively long time lag before it affects output, employment, and prices.
The central bank in the United States is the Federal Reserve System. It is often referred to as the "Fed" and is divided into twelve regions, administered by a Board of Governors in Washington, D.C. The three major policy tools available to the "Fed" are changing reserve ratios for banks, changing the discount rate of interest, and open market operations (OMO's). OMO's are the buying and selling of government securities in the open market. When the "Fed" buys securities, it increases the money supply and lowers interest rates. When it sells securities, it takes money out of circulation and raises interest rates. OMO's are the main monetary tool the "Fed" uses to promote price stability, economic growth, and full employment in the United States economy.
The other key central banks in the industrialized countries are shown
in the table below:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In The World Game of Economics you are the chief economic adviser to
the leaders of the country of your choice. You are in charge of economic
policy, including monetary policy. The objective is to implement
timely and appropriate economic polices to improve the overall economic
performance of your country. Good luck and have fun!
1. Play The World Game of Economics to 100 points against up to six other countries that are either computer-managed (i.e., advised by Professor N. D. Cator) or Laissez Faire . Note: If you do not know how to play the game, then select "Tutorial" from the main menu first. If you already know how to play, then select "New Game."
2. You are the chief economic adviser to which country?
_______________________.
3. How many other computer-managed countries are you playing
against? ________.
SOMETIME AFTER THE 3RD YEAR AND BEFORE THE 10TH YEAR OF THE GAME, COMPLETE THIS EXERCISE:
4. Which year have you chosen to complete this exercise?
__________.
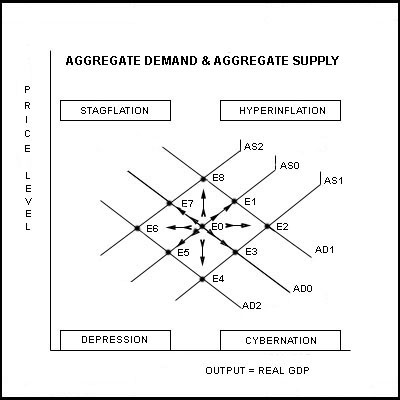
5. Look at the Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply diagram
below. Assuming your economy is at E0 at the beginning of your turn,
which direction is the Economic Indicator currently pointing: (Circle
One)
E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6 E7 E8

6. Which change or combination of changes in Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply does the direction of the Economic Indicator predict? (Circle One)
+AD +AD&+AS +AS -AD&+AS -AD -AD&-AS -AS +AD&-AS
Now click on ECONOMIC INDICATOR and the CURRENT EVENT. Click on ECONOMIC POLICY and go to the Policy Board. SELECT YOUR FISCAL AND TRADE POLICIES. DO NOT SELECT YOUR MONETARY POLICY, YET.
7. On the template below, indicate where your economy is currently positioned before selecting your monetary policy. Use a pen to sketch your country’s flag or print an abbreviation (e.g., USA = United States). Note: If you know how to use "Print Screen" tools, then use that method and attach to this exercise Circle the current position of your country.
8. Considering the current location of your country and the direction of the Economic Indicator, which Monetary Policy would you advise your central bank to undertake at this time? (Circle Only One).
+MS -MS +ms
-ms +BR -BR
none/pass
NOW SELECT YOUR MONETARY POLICY. COMPLETE THE GAME. Print the final score and attach it to this exercise.
ANSWER QUESTIONS 9 - 13. (Circle the letter before the best single answer).
9. If the economy is at full-employment and the central bank significantly
increases the money supply, it causes:
(a) interest rates to fall in the short-run, a decrease in aggregate
demand, and deflation.
(b) interest rates to fall in the short-run, an increase in aggregate
demand, and inflation.
(c) interest rates to rise in the short-run, an increase in aggregate
demand, and deflation.
(d) interest rates to rise in the short-run, an increase in aggregate
supply, and deflation.
(e) interest rates to fall in the short-run, a decrease in aggregate
supply, and inflation.
10. Which of the following statements regarding monetary policy is probably
true?
(a) Discretionary monetary policy is a very effective and precise policy
tool that can be used to fine tune the economy.
(b) Discretionary monetary policy is weak and ineffective, especially
against inflation.
(c) The longer the central bank waits to increase the money supply
when the economy is in a Depression, the less effective it becomes as a
counter-cyclical tool.
(d) The main cause of virtually all business cycles is ill-timed changes
in monetary policy.
(e) Implementation of monetary policy is frequently delayed by political
polemic.
11. Which of the following statements best describes how monetary policy
works?
(a) A change in the money supply affects bank liquidity and interest
rates, and changes in interest rates affect people's decisions regarding
spending and production.
(b) A change in the money supply affects the national debt, and changes
in the national debt cause people to spend more or less.
(c) A change in the money supply directly puts more or less currency
in people's pockets.
(d) The president tells the central bank what to do, and the central
bank does it.
(e) The central bank tells commercial banks what to do, and they do
it.
12. The most effective and frequently used monetary policy tool of the
central bank is:
(a) the discount rate, which is interest rate the central bank charges.
(b) the reserve ratio, which is the ratio of required reserves to bank
deposits.
(c) the margin requirement, which is the down payment required to buy
stocks.
(d) bank deregulation, which permits bank mergers and a greater variety
of services.
(e) open market operations, which is buying and/or selling government
securities.
13. Generally speaking (with some exceptions), your best strategy in
The World Game of Economics regarding monetary policy is to:
(a) always pass and not select a monetary policy, because the Economic
Indicator can change direction before your next turn.
(b) increase the money supply when you are in Stagflation, and
decrease it when you are in Cybernation.
(c) deregulate the banking industry when you are in a Depression, and
increase bank regulations when your economy has Hyperinflation.
(d) lean against the wind by selecting a monetary policy which will
move your country in the opposite direction of the Economic Indicator.
(e) select the monetary policy which does the most damage to your opponent(s).
End of Lesson 7
Note: At the instructor's discretion, you will receive _____ possible points for this exercise.
Instructor's Option: At the instructor's discretion, you may receive additional points according to the schedule below.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Examples: If you play against 6 other countries and you place 1st, then you get 10 extra points! If you play against 4 other countries and you place 3rd, then you get 6 extra points. If you play against two other countries and you place 2nd, then you get 5 extra points. In each case if you place last, then you get only 4 more points.
Winning Strategy Hints: Winning strategy involves anticipating the Economic Indicator, playing your policy options efficiently, coordinating your range of policies, and using trade policy to prevent one country from getting too far ahead. Consider your opponents’ options and try to anticipate their trade policies. Keep in mind that countries tend to use trade restrictions, tariffs, and currency devaluations when they have high unemployment. Be careful not to get caught having too many inappropriate and useless options. Discard policy gridlock and foreign policy conflict options as frequently as possible. [You don’t want to be trapped in a Depression like the United States in the 1930s or caught like Germany in Hyperinflation in the early 1920s]. Study the probabilities that are provided in the instructions. That will help you plan your strategy.
Global interdependency is portrayed both indirectly and directly in The World Game of Economics. Indirectly, when the Economic Indicator changes direction for one country, it changes direction for all the other countries. This demonstrates how economic recessions and recoveries are internationally contagious. When one country’s economy expands (or contracts), it begins to import more (or less) from other countries. Directly, one country’s trade policy affects another country. The two countries move in opposite directions. For example, when one country depreciates its currency vis-à-vis another country’s currency, exports increase in the former and decrease in the latter.
When planning your trade policy strategy, recall the other countries’ monetary policies. Note the direction of the Economic Indicator and consider which countries are leading in the game score. Try to move those countries away from the center at the same time that you improve your own country’s position.
The World Game of Economics (C) 1999 Ronald W. Schuelke
All Rights Reserved